What is Development?
Human Development or Lifespan Development is the scientific study of the ways in which people change, as well as remain the same, from conception to death. You will discover that the field, known more broadly as developmental science, examines changes and stability across multiple domains of psychological and social functioning. These include physical and neurophysiological processes, cognition, language, emotion, personality, moral, and psychosocial development, including our relationships with others.

Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence and more recently, aging and the entire life span. Previously, the message was once you are 25, your development is essentially completed. Our academic knowledge of the lifespan has changed, and although there is still less research on adulthood than on childhood, adulthood is gaining increasing attention. This is particularly true now that the large cohort known as the “baby boomers” are beginning to enter late adulthood. The assumption that early childhood experiences dictate our future is also being called into question. Instead, we have come to appreciate that growth and change continues throughout life and experience continues to have an impact on who we are and how we relate to others. We now recognize that adulthood is a dynamic period of life marked by continued cognitive, social, and psychological development.
You will also discover that developmental psychologists investigate key questions, such as whether children are qualitatively different from adults or simply lack the experience that adults draw upon. Other issues they consider include the question of whether development occurs through the gradual accumulation of knowledge or through qualitative shifts from one stage of thinking to another, or if children are born with innate knowledge or figure things out through experience, and whether development is driven by the social context or something inside each child. From these questions, you may already be thinking that developmental psychology is related to other applied fields. You are right. Developmental science informs many applied fields, including, educational psychology, developmental psychopathology, and intervention science. It also complements several other basic research fields in psychology including social psychology, cognitive psychology, and cross-cultural psychology. Lastly, it draws from the theories and research of several scientific fields including biology, sociology, health care, nutrition, and anthropology.
Learning Objectives: Lifespan Perspective
- Explain the lifespan perspective and its assumptions about development
- Differentiate periods of human development
- Identify key assumptions and major meta-theories underlying lifespan development
- Identify major historical and contemporary theories focusing on lifespan development
Lifespan Perspective
Paul Baltes identified several underlying principles of the lifespan perspective (Baltes, 1987; Baltes, Lindenberger, & Staudinger, 2006).
- Development is lifelong. Lifespan theorists believe that development is life-long, and change is apparent across the lifespan. No single age period is more crucial, characterizes, or dominates human development. Consequently, the term lifespan development will be used throughout the textbook.
- Development is multidirectional and multidimensional. Lifespan researchers hold that different people follow different developmental pathways, and proceed along pathways at different rates. Even within the same person, different dimensions or domains of development can change in different ways.
- Development includes both gains and losses. Lifespan theorists do not agree with the traditional view of development that childhood is a period characterized by developmental gains, whereas old age is a time of loss. Instead, the lifespan approach holds that at every age, we may show gains in some areas of development, while showing losses in other areas. Every change, whether it is finishing high school, getting married, or becoming a parent, entails both growth and loss.
- Development is characterized by plasticity. Plasticity is about malleability, or our potential to change and to follow a wide range of developmental pathways. For instance, plasticity is illustrated in the brain’s ability to learn from experience and the many ways it can recover from injury.
- Development is embedded in historical and cultural contexts. Lifespan researchers believe that development is influenced by the many social contexts in which it unfolds. How people develop will depend on their societal and cultural contexts, and on the historical period during which their development takes place.
- Development is multiply determined. Lifespan theorists argue that development is caused by multiple factors, and is always shaped by both biological and environmental factors. In addition, the individual plays an active role in their own development.
- Development is multidisciplinary. As mentioned at the start of the chapter, human development is such a vast topic of study that it requires the theories, research methods, and knowledge bases of many academic disciplines.
Contextualism as paradigm. Baltes (1987) identified three specific developmental systems of influence, all of which include biological and environmental forces.
-
- Normative age-graded influences: An age-grade is a specific age group, such as toddler, adolescent, or senior. Humans experience particular age-graded social experiences (e.g., starting school) and biological changes (e.g., puberty).
- Normative history-graded influences: The time period in which you are born (see Table 1.1) shapes your experiences. A cohort is a group of people who are born at roughly the same period in a particular society. These people travel through life often experiencing similar historical changes at similar ages. History-graded influences include both environmental determinants (e.g., historical changes in the job market) and biological determinants (e.g., historical changes in life expectancy).
- Non-normative influences: People’s development is also shaped by specific influences that are not organized by age or historical time, such as immigration, accidents, or the death of a parent. These can be environmental (e.g., parental mental health issues) or biological (e.g., life threatening illness).
Table 1.1. Which generation (cohort) are you?
| Generation | Born between... |
|---|---|
| Silent Generation | 1928 and 1945 |
| Baby Boomers | 1946 and 1964 |
| Generation X | 1965 and 1980 |
| Millenials | 1982 and 1996 |
| Generation Z | 1997 and 2009 |
| Generation Alpha | 2010 and 2024 |
adapted from Lally & Valentine-French, 2019
Domains of development. We change across three general domains/dimensions; physical, cognitive, and psychosocial. The physical domain includes changes in height and weight, sensory capabilities, the nervous system, as well as the propensity for disease and illness. The cognitive domain encompasses the changes in intelligence, wisdom, perception, problem-solving, memory, and language. The psychosocial domain focuses on changes in emotion, self-perception and interpersonal relationships with families, peers, and friends. All three domains influence each other. It is also important to note that a change in one domain may cascade and prompt changes in the other domains. For instance, an infant who has started to crawl or walk will encounter more objects and people, thus fostering developmental change in the child’s understanding of the physical and social world.
Contextual perspectives, like the lifespan approach, highlight societal contexts that influence our development. An important societal factor is our social standing, socioeconomic status, or social class. Socioeconomic status (SES) is a way to identify families and households based on their shared levels of education, income, and occupation. While there is certainly individual variation, members of a social class tend to share similar privileges, opportunities, lifestyles, patterns of consumption, parenting styles, stressors, religious preferences, and other aspects of daily life. All of us born into a class system are socially located, and we may move up or down depending on a combination of both socially and individually created limits and opportunities.
Families with higher socioeconomic status usually are in occupations (e.g., attorneys, physicians, executives) that not only pay better, but also grant them a certain degree of freedom and control over their job. Having a sense of autonomy or control is a key factor in experiencing job satisfaction, personal happiness, and ultimately health and well-being (Weitz, 2007). Those families with lower socioeconomic status are typically in occupations that are more routine, more heavily supervised, and require less formal education. These occupations are also more subject to job disruptions, including lay-offs and lower wages.
Poverty level is an income amount established by the federal government that is based on a set of thresholds that vary by family size (United States Census Bureau, 2016). If a family’s income is less than the government threshold, that family is considered in poverty. Those living at or near poverty level may find it extremely difficult to sustain a household with this amount of income. Poverty is associated with poorer health and a lower life expectancy due to poorer diet, less healthcare, greater stress, working in more dangerous occupations, higher infant mortality rates, poorer prenatal care, greater iron deficiencies, greater difficulty in school, and many other problems. Members of higher income status may fear losing that status, but the poor may have greater concerns over losing housing.
Today we are more aware of the variations in development and the impact that culture and the environment have on shaping our lives. Culture is the totality of our shared language, knowledge, material objects, and behavior. It includes ideas about what is right and wrong, what to strive for, what to eat, how to speak, what is valued, as well as what kinds of emotions are called for in certain situations. Culture teaches us how to live in a society and allows us to advance because each new generation can benefit from the solutions found and passed down from previous generations. Culture is learned from parents, schools, houses of worship, media, friends and others throughout a lifetime. The kinds of traditions and values that evolve in a particular culture serve to help members function and value their own society. We tend to believe that our own culture’s practices and expectations are the right ones. This belief that our own culture is superior is called ethnocentrism and is a normal by-product of growing up in a culture. It becomes a roadblock, however, when it inhibits understanding of cultural practices from other societies. Cultural relativity is an appreciation for cultural differences and the understanding that cultural practices are best understood from the standpoint of that particular culture.
Culture is an extremely important context for human development and understanding development requires being able to identify which features of development are culturally based. This understanding is somewhat new and still being explored. Much of what developmental theorists have described in the past has been culturally bound and difficult to apply to various cultural contexts. The reader should keep this in mind and realize that there is still much that is unknown when comparing development across cultures.
Lifespan vs. Life expectancy: At this point you must be wondering what the difference between lifespan and life expectancy is, according to developmentalists. Lifespan, or longevity, refers to the maximum age any member of a species can reach under optimal conditions. For instance, the grey wolf can live up to 20 years in captivity, the bald eagle up to 50 years, and the Galapagos tortoise over 150 years (Smithsonian National Zoo, 2016). The longest recorded lifespan for a human was Jean Calment who died in 1994 at the age of 122 years, 5 months, and 14 days (Guinness World Records, 2016). Life expectancy is the average number of years a person born in a particular time period can typically expect to live (Vogt & Johnson, 2016).
Conceptions of Age
How old are you? Chances are you would answer that question based on the number of years since your birth, or what is called your chronological age. Ever felt older than your chronological age? Some days we might “feel” like we are older, especially if we are not feeling well, are tired, or are stressed out. We might notice that a peer seems more emotionally mature than we are, or that they are physically more capable. So years since birth is not the only way we can conceptualize age.
Biological age: Another way developmental researchers can think about the concept of age is to examine how quickly the body is aging, this is your biological age. Several factors determine the rate at which our body ages. Our nutrition, level of physical activity, sleeping habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, how we mentally handle stress, and the genetic history of our ancestors, to name but a few.
Psychological age: Our psychologically adaptive capacity compared to others of our chronological age is our psychological age. This includes our cognitive capacity along with our emotional beliefs about how old we are. An individual who has cognitive impairments might be 20 years of age, yet has the mental capacity of an 8-year-old. A 70- year-old might be travelling to new countries, taking courses at college, or starting a new business. Compared to others of our age group, we may be more or less active and excited to meet new challenges. Remember you are as young or old as you feel.
Social age: Our social age is based on the social norms of our culture and the expectations our culture has for people of our age group. Our culture often reminds us whether we are “on target” or “off target” for reaching certain social milestones, such as completing our education, moving away from home, having children, or retiring from work. However, there have been arguments that social age is becoming less relevant in the 21st century (Neugarten, 1979; 1996). If you look around at your fellow students at college you might notice more people who are older than traditional aged college students, those 18 to 25. Similarly, the age at which people are moving away from the home of their parents, starting their careers, getting married or having children, or even whether they get married or have children at all, is changing.
Those who study lifespan development recognize that chronological age does not completely capture a person’s age. Our age profile is much more complex than this. A person may be physically more competent than others in their age group, while being psychologically immature. So, how old are you?
Table 1.2 Age Periods of Development
| Age Period | Description |
|---|---|
| Prenatal | Starts at conceptions, continues through implantation in the uterine wall by the embryo, and ends at birth. |
| Infancy and Toddlerhood | Starts at birth and continues to two years of age. |
| Early Childhood | Starts at two years of age until six years of age. |
| Middle and Late Childhood | Starts at six years of age and continues until the onset of puberty. |
| Adolescence | Starts at the onset of puberty until 18 |
| Emerging Adulthood | Starts at 18 until 25. |
| Early Adulthood | Starts at 25 until 40-45. |
| Late Adulthood | Starts at 65 onward. |
adapted from Lally & Valentine-French, 2019
Table 1.2 shows the developmental periods that will be explored in this book, starting with prenatal development and continuing thought late adulthood to death. Both childhood and adulthood are divided into multiple developmental periods. So, while both an 8-month old and an 8-year-old are considered children, they have very different motor abilities, social relationships, and cognitive skills. Their nutritional needs are different and their primary psychological concerns are also distinctive. The same is true of an 18-year-old and an 80-year-old, even though both are considered adults.
Prenatal Development: Conception occurs and development begins. All of the major structures of the body are forming, and the health of the mother is of primary concern. Understanding nutrition, teratogens, or environmental factors that can lead to birth defects, and labor and delivery are primary concerns.

Infancy and Toddlerhood: The first two years of life are ones of dramatic growth and change. A newborn, with a keen sense of hearing but very poor vision, is transformed into a walking, talking toddler within a relatively short period of time. Caregivers are also transformed from someone who manages feeding and sleep schedules to a constantly moving guide and safety inspector for a mobile, energetic child.
Early Childhood: This period is also referred to as the preschool years and consists of the years that follow toddlerhood and precede formal schooling. As a two to six-year-old, the child is busy learning language, gaining a sense of self and greater independence, and beginning to understand the workings of the physical world.
Middle and Late Childhood: The ages of six to the onset of puberty comprise middle and late childhood, and much of what children experience at this age is connected to their involvement in the early grades of school. Now the world becomes one of learning and testing new academic skills, and assessing one’s abilities and accomplishments by making comparisons between self and others.
Adolescence: Adolescence is a period of dramatic physical change marked by an overall growth spurt and sexual maturation, known as puberty. It is also a time of cognitive change as the adolescent begins to think of new possibilities and to consider abstract concepts such as love, fear, and freedom. At the same time, adolescents have a sense of invincibility that puts them at greater risk of accidents or contracting sexually transmitted infections that can have lifelong consequences.
Emerging Adulthood: The period of emerging adulthood is a transitional time between the end of adolescence and before individuals acquire all the benchmarks of adulthood. Continued identity exploration and preparation for full independence from parents are negotiated. Although at one’s physiological peak, emerging adults are most at risk for involvement in violent crimes and substance abuse.
Early Adulthood: The twenties and thirties are identified as early adulthood. Intimate relationships, establishing families (of all shapes and sizes), and work are primary concerns at this stage of life. For adults with children, developmental changes can become organized around the family life cycle.

Middle Adulthood: The forties through the mid-sixties are referred to as middle adulthood. This is a period in which aging becomes more noticeable and when many people are at their peak of productivity in love and work. At this age, some people are negotiating adolescent children and aging parents at the same time.
Late Adulthood: Late adulthood is sometimes subdivided into two categories: The young-old who are from 65-84 years and the oldest-old who are 85 years and older. One of the primary differences between these groups is that the young-old are still relatively healthy, productive, active, and the majority continue to live independently. With both age groups the risks of diseases such as arteriosclerosis, cancer, and cerebral vascular disease increase substantially.
Meta-theories of Human Development
The study of development is guided by the assumptions researchers hold about the nature of humans and their development. These assumptions are called meta-theories. “Meta” means “above” or “beyond,” like “meta-physics.” Other terms used to describe meta-theories are “world views,” “cosmologies,” “perspectives,” or “paradigms,” as in “paradigm shifts.” Explicit discussions of meta-theories are found most often in philosophy.
What are meta-theories of human development?
Meta-theories (or world views or paradigms) of human development are sets of assumptions people hold about the nature of humans and the meaning of development— what it looks like, how it happens, what causes it. These assumptions are important because everyone has them, including researchers, but they are often implicit, meaning we are not always consciously aware of them. In the study of development, such assumptions influence everything about how research is conducted: the questions we ask, the measures and methods that are used, and the interpretation of data. For example, if researchers assume that development ends at 18, they do not look for developmental changes after that age. Or, if researchers assume that aging is a process of decline, then they never look for characteristics that might improve as people get older.
All researchers have meta-theories, since assumptions are baked into the theories and methodologies they use. But researchers are often unaware of them, and so these assumptions are rarely acknowledged. It is important to note that meta-theories are not just cold cognitions. They are often deeply held convictions that researchers will fiercely defend. Typically researchers think that their assumptions are self-evident truths. They are often convinced that their assumptions are right and everyone else’s are wrong.
Researchers holding different meta-theories can have difficulty communicating with each other. Since they are asking different questions and using different truth criteria for research, they often argue past each other or misunderstand each other. One group of researchers will offer what they consider to be irrefutable proof of their ideas, which other researchers then dismiss as irrelevant. Discrepancies, inconsistencies, arguments, and furor often characterize an area of study in which researchers from multiple meta-theories are working.
What kinds of assumptions guide the study of human development?
We consider six key assumptions. You may have heard of many of them, since they are perennial issues in the study of development. They include:
- Assumptions about human nature: whether people are born as blank slates (tabula rasa) or whether people are inherently good or inherently bad.
- Assumptions about the causes of development: whether development is determined by nature (genes, biology) or determined by nurture (environment, learning).
- Assumptions about the role of the individual in his or her own development: whether people are passive participants, reacting to external forces or whether they are active in choosing and shaping their own development.
- Assumptions about stability vs. change: whether traits, characteristics, and experiences early in life have permanent effects or whether people are malleable and open to change throughout life.
- Assumptions about continuity vs. discontinuity: whether development involves quantitative incremental change or qualitative shifts.
- Assumptions about universality vs. context specificity: whether development follows a universal pathway or depends more on specific experiences and environmental contexts.
Nature of humans. What is the nature of humans? These assumptions refer to beliefs about the underlying qualities of our species– whether humans are born as blank slates (tabula rasa) or whether we all bring intrinsic human characteristics with us into the world. For example, these different assumptions are readily apparent in alternative conceptualizations of motivation—some theories assume that motives and motivation are all acquired, whereas others assume that all humans come with intrinsic motivations.
Nature and Nurture: Why are you the way you are? As you consider some of your features (height, weight, personality, being diabetic, etc.), ask yourself whether these features are a result of heredity or environmental factors, or both. Chances are, you can see the ways in which both heredity and environmental factors (such as lifestyle, diet, and so on) have contributed to these features. For decades, scholars have carried on the “nature/nurture” debate. For any particular feature, those on the side of nature would argue that heredity plays the most important role in bringing about that feature. Those on the side of nurture would argue that one’s environment is most significant in shaping the way we are. This debate continues in all aspects of human development, and most scholars agree that there is a constant interplay between the two forces. It is difficult to isolate the root of any single behavior as a result solely of nature or nurture.
Active versus Passive: How much do you play a role in your own developmental path? Are you at the whim of your genetic inheritance or the environment that surrounds you? Some theorists see humans as playing a much more active role in their own development. Piaget, for instance believed that children actively explore their world and construct new ways of thinking to explain the things they experience. In contrast, many behaviorists view humans as being more passive in the developmental process.
Stability versus Change: How similar are you to how you were as a child? Were you always as out-going or reserved as you are now? Some theorists argue that the personality traits of adults are rooted in the behavioral and emotional tendencies of the infant and young child. Others disagree, and believe that these initial tendencies are modified by social and cultural forces over time.
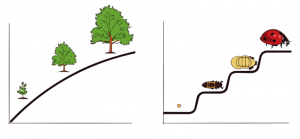
Continuity versus Discontinuity: Is human development best characterized as a slow, gradual process, or is it best viewed as one of more abrupt change? The answer to that question often depends on which developmental theorist you ask and what topic is being studied. The theories of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, and Kohlberg are called stage theories. Stage theories or discontinuous development assume that developmental change occurs in distinct stages that are qualitatively different from each other, and that unfold in a set, universal sequence. At each stage of development, children and adults have different qualities and characteristics. Thus, stage theorists assume development is discontinuous. Others, such as the behaviorists, Vygotsky, and information processing theorists, assume development is a more slow and gradual process known as continuous development. For instance, they would see the adult as not possessing new skills, but as using more advanced skills that were already present in some form in the child. Brain development and environmental experiences contribute to the acquisition of more developed skills.
Universal vs. context specific. A final assumption focuses on whether pathways of development are presumed to be (1) normative and universal, meaning that all people pass through them in the same sequence, or (2) differential and specific, meaning that a variety of different patterns and pathways of developmental change are possible depending on the individual and the context. Some theorists, like Piaget or Erickson, assume that everyone progresses through the same stages of cognitive development in the same order, or that everyone negotiates the same set of developmental tasks at about the same ages. Other theorists, who endorse lifespan or ecological systems approaches, believe that development can take on a wide variety of patterns and pathways, depending on the specific cultural, historical, and societal under which it unfolds.
What are the guiding meta-theories in human development?
These six basic assumptions are clustered into “packages” that go together. Clusters are organized around metaphors, which are at the root of meta-theories of humans and their development. We consider four meta-theories, each with its own metaphor: (1) humans as seeds, as depicted by Maturational meta-theories; (2) humans as machines, as depicted in Mechanistic meta-theories (3) humans as butterflies, as depicted in Organismic meta-theories; and (4) humans as participants in a tennis game, conversation, or dance, as depicted by Contextualist meta-theories. For an overview of these guiding meta-theories, see this chart [pdf].
- Maturational meta-theory: Maturational meta-theories can be understood using the plant as a metaphor. It is as if humans develop the same way as plants. The important thing to study is people’s “seeds,” that is, their genetic make-up. People are assumed to be passive, the product of their genes. The environment can provide support and nutrition (rain, sun, and soil), but can’t change a person’s nature (poppy seeds will always produce poppies). The role of the person is to be reactive—to their genes. The course of development will be continuous or discontinuous depending on the genetic program, although acorns always grow into oak trees.
- Mechanistic meta-theory: Mechanistic meta-theories can be understood using the machine as a metaphor. It is as if humans change the same way as machines. People are assumed to be made up of pieces that can be studied apart from the rest of them. They are passive, with the energy coming from outside (like gasoline for a car). Development is continuous and people do not develop into something else (a car stays a car). The person can only react to the environment that is controlling them (like a car responding to the gas pedal or the brake). All causes for development come from the outside, from environmental forces.
- Organismic meta-theory: Organismic meta-theories can be understood using the butterfly as a metaphor. It is as if humans develop the same way as butterflies. People are assumed to be made up of structured wholes. Their nature is to be curious, interested, and open to growth. They are active and develop through discontinuous qualitatively different stages (like the caterpillar, chrysalis, and butterfly). People construct their own next steps in development based on the affordances and opportunities provided by the environment. Development is caused by imbalances that lead to structural reorganizations. Development is progressive (gets better) and only goes in one direction (from caterpillar toward butterfly) and not the reverse.
- Contextual meta-theory: Contextual meta-theories can be understood using the tennis game (or dance) as a metaphor. It is as if humans’ development is like a game of tennis or a dance. The important thing to study is the back and forth between the person and his or her context, both of which are assumed to be proactive and acting on their own agendas. Development can be continuous or discontinuous depending on how the game is played. Both person and environment are active partners in the system, which can lead to transformations in both.
What are examples of theories that fall within each meta-theory?
Nested within each higher-order meta-theory are sets of lower-level approaches or theories called “families” of perspectives or theories to denote that they share common properties, based on their similarity to the root metaphors and characteristics of the guiding meta-theories. This table contains several examples of “big” theories of development and provides an analysis of their defining features according to the meta-theoretical assumptions we have been discussing [pdf]. Based on this analysis, we indicate the higher-order family to which we think each big theory or approach belongs.
Although maturational meta-theories were prevalent in the beginning of the 20th century, their popularity has waxed and waned since then, and they have taken on many different forms. These include some formulations of behavioral genetics, sociobiology, evolutionary, ethological, neuroscience, temperament, and personality theories. Maturational assumptions are signaled by concepts such as “trait,” the search for “the aggression gene,” the discovery of the brain system, hormone, or neurotransmitter responsible for a specific condition, or any other terms that suggest development is solely the product of innate or immutable characteristics of individuals. Although they are not typically referred to as “maturational,” there are many kinds of theories that place all the active ingredients of behavior or development inside the head (or more specifically the social cognitions) of the person. Even if they are not direct descendants, these theories can be considered cousins of Maturational meta-theories because they are exclusively focused on the role of the individual.
The prototypic Mechanistic theories are behaviorist, operant, and classical conditioning learning theories, like social learning theory. This family of theories dominated psychology from the early to the mid-20th century, but Mechanistic theories are still alive and well in many areas, such as learning and motivation, and especially in many theories that have been adapted for use in educational systems. New kinds of machines serve as prototypes for mechanistic theories of memory, learning, and automatic functioning—focusing on the computer, the robot, and the automaton. Such assumptions have even pervaded our understanding of biological systems, as seen in metaphors like “the brain is a computer.” And although the “cognitive revolution” was supposed to have overthrown behaviorist assumptions, some cognitivistic theories treat humans as if they were information processing machines.
Perhaps surprisingly, there are also mechanistic assumptions embedded in certain progressive analyses of the effects of societal and social conditions, such as poverty, oppression, racism, and discrimination, which sometimes seem to imply that these external forces are the sole determinants of the development of stereotypes or implicit attitudes. In this case, because all people are presumed to passively internalize these societal prejudices, psychological phenomena are modeled after the metaphor of the “Xerox machine.” Just as in Maturational meta-theories, where humans could be seen as “hosts” to their genes, who were really running the show, in Mechanistic meta-theories, humans can be seen as “hosts” to their own behaviors, which are automatically reflexively produced based on previous social programming.
The prototypical Organismic theory is Piaget’s constructivist theory of cognitive and affective development, and the several neo-constructivist theories that were inspired by Piaget, for example, Kohlberg’s theory of the development of moral reasoning. Other theories living under the Organismic umbrella include Werner’s comparative psychology, focusing on the orthogenetic principle of differentiation and integration, and Erikson, who posited universal age-graded developmental tasks. Other theories that claim kinship with Organismic meta-theories (e.g., theories of intrinsic motivation) do not typically include notions of universal stages or tasks, but focus instead on Organismic assumptions about the nature of humans, specifically, that humans are innately active, curious, and interested, and inherently desire to explore, understand, and fit in with their social and physical environments. With the rise of radical contextualism and cultural relativism in psychology, theories of “universal” anything (e.g., psychological needs, stages, developmental tasks) have come increasingly under attack.
Some of the better-known members of the Contextualist family include Bronfenbrenner’s bio-ecological model and the lifespan approach, both of which arose in reaction to dominant meta-theories of their day (experimental child psychology and Piagetian psychology, respectively), with their almost exclusive focus on the child as a developing individual. The “contextualist” moniker reflects these perspectives’ insistence that development unfolds within and is shaped by higher-order multi-level ecological or contextual forces outside the individual, such as microsystem settings, and societal, cultural, and historical contexts.
Does the field of psychology have meta-theories?
During different historical periods, specific meta-theories dominated the field of psychology. For example, during the 1940s and 1950s, behaviorism held sway. In the 1960s, Piaget’s theories were introduced to the United States and captured the field’s attention. Some fierce theoretical and empirical battles were fought between behaviorists and Piagetians.
When a specific meta-theory governs the field, it becomes very difficult for researchers from opposing meta-theories to work—they have trouble getting funding, they have trouble getting their research findings published, and they are marginalized by other researchers. For example, when the area of motivation was dominated by behaviorists (who believed that all behavior was motivated by rewards and punishments), it was very difficult for researchers to study and publish research on intrinsic motivation.
What is the dominant meta-theory in the field today?
“Cognitivism” is a guiding meta-theory in the field of psychology today. “Cognitivism” is the assumption that all the causal factors that shape human behavior and development are inside the mind or belief system of the person. You can hear the assumptions in the theories of the field: self-efficacy, self-esteem, attributions, perceived social support, values, sense of purpose, goal orientations, internal working model, identity, and so on.
The paradigm that is currently taking over the field of psychology is neuroscience. That is, the brain is in charge of behavior, and neurobiology is destiny. Some branches of neuroscience are predominantly Maturational, as seen in discussions of the brain systems responsible for certain actions, predilections, and characteristics. Other branches are more Contextual, for example, research on neuroplasticity, which examines the way that social contexts and interactions shape the developing brain.
News flash: In the field of psychology outside developmental, most researchers assume that people don’t develop. In personality, social, cognitive, and industrial-organizational psychology, researchers largely examine individual differences as indicators of people’s permanent characteristics.
Who else has meta-theories?
Everyone has meta-theories about human nature and development: parents, teachers, nurses, social workers, doctors, business people, artists, politicians, and so on.
For example,
- doctors assume that weight loss is all about diet and exercise (nurture), so no one can do research on physiological differences in metabolism (nature).
- teachers have assumptions about whether students come with motivation (nature) or have to be motivated from the outside (nurture), and organize their classrooms accordingly.
- parents often argue about the nature of children’s development, whether it’s just the child’s personality (maturational), or the child is going through a normal stage (organismic), or if they are rewarding the wrong behavior (mechanistic).
What is the meta-theory that guides our class and this book?
Our class endorses a life-span perspective on human development, a contextualist perspective that fought its way through the dominant perspectives in child psychology (e.g., development ends at age 18), starting in the 1980s to become one of the dominant meta-theories governing the field of developmental science today. Note that your instructors chose your book, so their meta-theory is influencing the meta-theoretical filter through which you are learning about development.
What is the correct meta-theory?
There is no single correct definition of development or meta-theory. Really. Even the lifespan approach has its drawbacks.
However, as research accumulates, many theories derived from certain meta-theories have been found to be incomplete—so far researchers have not found any significant aspect of development that is caused only by nature or only by nurture. Therefore, most researchers currently say they favor interactionist metatheories, like contextualist or systems meta-theories. However, it is important to look carefully at researchers’ actual work, because sometimes they say that they have one meta-theory, but their work seems to be guided by assumptions from a different meta-theory.
Do I have a meta-theory about development?
Yes, you do. And you can figure out what it is. Although it’s not easy, you can discern your own assumptions about development—by thinking about which assumptions make the most sense to you. You can also see which kinds of theories you prefer and what kinds of recommendations you would make about how to structure development, like how people should parent, teach, or make policies. The hardest part about discovering your own meta-theory is realizing that it is made up of assumptions you have (based on your experiences and messages from society)—that aren’t necessarily true. Our meta-theories sure seem true to each of us!
How do I get rid of my meta-theory?
It’s not really possible to get rid of all of our assumptions. It is our goal to be aware of our own assumptions or meta-theories, to realize that they are not the truth but are our current working models of how the world operates and people develop. The most important thing is to be explicit about our assumptions and to be cognizant of how they are guiding our actions. It is a goal of this class to help students figure out their own assumptions and to help them become (or remain) open to alternative viewpoints.
Adapted from: Ellen Skinner, Glen Richardson, Jennifer Pitzer, and Cynthia Taylor. Portland State University. July 2011.
Historical Theories of Development
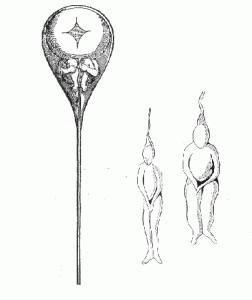
Preformationist View: Well into the 18th century, children were merely thought of as little adults. Preformationism, or the belief that a tiny, fully formed human is implanted in the sperm or egg at conception and then grows in size until birth, was the predominant early theory. Children were believed to possess all their sensory capabilities, emotions, and mental aptitude at birth, and as they developed these abilities unfolded on a predetermined schedule (Thomas, 1979). The environment was thought to play no role in determining development.
John Locke (1632-1704): Locke, a British philosopher, refuted the idea of innate knowledge and instead proposed that children are largely shaped by their social environments, especially their education as adults teach them important knowledge. He believed that through education a child learns socialization, or what is needed to be an appropriate member of society. Locke advocated thinking of a child’s mind as a tabula rasa or blank slate, and whatever comes into the child’s mind comes from the environment. Locke emphasized that the environment is especially powerful in the child’s early life because he considered the mind the most pliable then. Locke indicated that the environment exerts its effects through associations between thoughts and feelings, behavioral repetition, imitation, and rewards and punishments (Crain, 2005). Locke’s ideas laid the groundwork for the behavioral perspective and subsequent learning theories of Pavlov, Skinner and Bandura.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778): Like Locke, Rousseau also believed that children were not just little adults. However, he did not believe they were blank slates, but instead developed according to a natural plan which unfolded in different stages (Crain, 2005). He did not believe in teaching them the correct way to think, but believed children should be allowed to think by themselves according to their own ways and an inner, biological timetable. This focus on biological maturation resulted in Rousseau being considered the father of developmental psychology. Followers of Rousseau’s developmental perspective include Gesell, Montessori, and Piaget.
Arnold Gesell (1880-1961): Gesell spent 50 years at the Yale Clinic of Child Development, and with his colleagues he studied the neuromotor development of children. Gesell believed that the child’s development was activated by genes and he called this process maturation (Crain, 2005). Further, he believed that development unfolded in fixed sequences, and he opposed efforts to teach children ahead of schedule as he believed they will engage in behaviors when their nervous systems had sufficiently matured.

Sigmund Freud (1856-1939): Freud was a very influential figure in the area of development. Freud emphasized the importance of early childhood experiences in shaping our personality and behavior. In our natural state, we are biological beings and are driven primarily by instincts. During childhood, however, we begin to become social beings as we learn how to manage our instincts and transform them into socially acceptable behaviors. His assumptions were that personality formed during the first few years of life. The ways in which parents or other caregivers interacted with children were assumed to have a long-lasting impact on children’s emotional states. His beliefs formed the psychodynamic perspective and his theories of psychosexual development and psychopathology dominated the field of psychiatry until the growth of behaviorism in the 1950s.
However, Freud’s theory has been heavily criticized for several reasons. One is that it is very difficult to test scientifically (Crews, 1998). Freud suggested that much of what determines our actions were unknown to us, and as scientists we cannot measure these unconscious concepts. A second criticism is that Freud’s case studies were not validated and cannot be used as evidence for his theories. Many later theories, particularly behaviorism and humanism, came about as challenges to Freud’s views.
Contemporary Theories on Development

Erikson (1902-1994) and Psychosocial Theory: Now, let’s turn to a less controversial psychodynamic theorist, Erik Erikson. Erikson presents eight developmental stages that encompass the entire lifespan. For that reason, Erikson’s psychosocial theory forms the foundation for much of our discussion of psychosocial development.
Erikson (1950) proposed a model of lifespan development that provides a useful guideline for thinking about the changes we experience throughout life. Erikson broke with Freud’s emphasis on sexuality as the cornerstone of social-emotional development and instead suggested that social relationships fostered development. Erikson proposed that each period of life has a unique challenge or crisis that the person who reaches it must face, referred to as psychosocial crises. According to Erikson, successful development involves dealing with and resolving the goals and demands of each of these psychosocial crises in a positive way. These crises are usually called stages, although that is not the term Erikson used. If a person does not resolve a stage successfully, it may hinder their ability to deal with later stages. For example, the person who does not develop a sense of trust (Erikson’s first stage) may find it challenging as an adult to form a positive intimate relationship (Erikson’s sixth stage). Or an individual who does not develop a clear sense of purpose and identity (Erikson’s fifth stage) may become self-absorbed and stagnate rather than work toward the betterment of others (Erikson’s seventh stage).
However, most individuals are able to successfully complete the eight stages of his theory (See Table 1.3).
Table 1.3 Erikson's Psychosocial Stages
| Age range | Psychosocial crisis | Positive resolution of crisis |
|---|---|---|
| Birth to 12 to 18 months | Trust versus Mistrust | The child develops a feeling of trust in caregivers. |
| 18 months to 3 years | Autonomy versus Shame/Doubt | The child learns what can and cannot be controlled and develops a sense of free will. |
| 3 to 6 years | Initiative versus Guilt | The child learns to become independent by exploring, manipulating, and taking action. |
| 6 to 12 years | Industry versus Inferiority | The child learns to do things well or correctly according to standards set by others, particularly in school. |
| 12 to 18 years | Identity versus Role Confusion | The adolescent develops a well-defined and positive sense of self in relationship to others. |
| 19 to 40 years | Intimacy versus Isolation | The person develops the ability to give and receive love and to make long-term commitments. |
| 40 to 65 years | Generativity versus Stagnation | The person develops an interest in guiding the development of the next generation, often by becoming a parent. |
| 65 to death | Ego Integrity versus Despair | The person develops acceptance of how one has lived. |
adapted from Lally & Valentine-French, 2019
Erikson’s theory has been criticized for focusing so heavily on crises and assuming that the completion of one crisis is a prerequisite for the next crisis of development. His theory also focused on the social expectations that are found in certain cultures, but not in all. For instance, the idea that adolescence is a time of searching for identity might translate well in the middle-class culture of the United States, but not as well in cultures where the transition into adulthood coincides with puberty through rites of passage and where adult roles offer fewer choices.
Learning Theory: Also known as Behaviorism, is based on the premise that it is not possible to objectively study the mind, and therefore psychologists should limit their attention to the study of behavior itself. The most famous behaviorist was Burrhus Frederick (B. F.) Skinner (1904–1990), who expanded the principles of behaviorism and also brought them to the attention of the public at large. Skinner used the ideas of stimulus and response, along with the application of rewards or reinforcements, to train pigeons and other animals. In addition, he used the general principles of behaviorism to develop theories about how best to teach children and how to create societies that were peaceful and productive (Skinner, 1957, 1968, 1972).
The behaviorists made substantial contributions to psychology by identifying the principles of learning. Although the behaviorists were incorrect in their beliefs that it was not possible to measure thoughts and feelings, their ideas provided new insights that helped further our understanding regarding the nature-nurture debate as well as the question of free will. The ideas of behaviorism are fundamental to psychology and have been developed to help us better understand the role of prior experiences in a variety of areas of psychology.
Social Learning Theory, or learning by watching others, was developed by Albert Bandura (1977). His theory calls our attention to the ways in which many of our actions are not learned through conditioning, as suggested by Skinner. Young children frequently learn behaviors through imitation. Especially when children do not know what else to do, they learn by modeling or copying the behavior of others.
Bandura (1986) suggests that there is interplay between the environment and the individual. We are not just the product of our surroundings, rather we influence our surroundings. There is interplay between our personality and the way we interpret events and how they influence us. This concept is called reciprocal determinism. An example of this might be the interplay between parents and children. Parents not only influence their child’s environment, perhaps intentionally through the use of reinforcement, etc., but children influence parents as well. Parents may respond differently with their first child than with their fourth. Perhaps they try to be the perfect parents with their firstborn, but by the time their last child comes along they have very different expectations, both of themselves and their child. Our environment creates us and we create our environment.
Other social influences: TV or not TV? Bandura, Ross and Ross (1963) began a series of studies to look at the impact of television on the behavior of children. Bandura began by conducting an experiment in which he showed children a film of a woman hitting an inflatable clown or “bobo” doll. Then the children were allowed in the room, where they found the doll and during their play they began to hit it. The children also demonstrated novel ways of being aggressive toward the doll that were not demonstrated by those children who did not see the aggressive model. Bandura’s research raised concerns about the impact of violence on young children. Since then, considerable research has been conducted on the impact of violent media on children’s aggression including playing video games.
Cognitive Theory: The cognitive theories focus on how our mental processes or cognitions change over time. Three important theories are Jean Piaget’s, Lev Vygotsky’s, and Information-processing.
Jean Piaget (1896-1980) was one of the most influential cognitive theorists in development. He was inspired to explore children’s ability to think and reason by watching his own children’s development. He was one of the first to recognize and map out the ways in which children’s intelligence differs from that of adults (Piaget, 1929). He became interested in this area when he was asked to test the IQ of children and began to notice that there was a pattern in their wrong answers. He believed that children’s intellectual skills change over time and that maturation, rather than training, brings about that change. Children of differing ages interpret the world differently. Piaget theorized that children progressed through four stages of cognitive development (see Table 1.4).
Table 1.4 Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development
| Stage | Approximate age range | Characteristics | Stage attainments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensorimotor | Birth to about 2 years | Children experience the world through their fundamental senses of seeing, hearing, touching, and tasting. | Object permanence |
| Preoperational | 2 to 7 years | Children acquire the ability to internally represent the world through language and mental imagery. They also start to see the world from other people’s perspectives. | Theory of mind; rapid increase in language ability |
| Concrete operational | 7 to 11 years | Children become able to think logically. They can increasingly perform operations on objects that are real | Conservation |
| Formal operational | 11 years to adulthood | Adolescents can think systematically, can reason about abstract concepts, and can understand ethics and scientific reasoning. | Abstract logic |
adapted from Lally & Valentine-French, 2019
Piaget has been criticized for overemphasizing the role that physical maturation plays in cognitive development and in underestimating the role that culture and experience plays. Looking across cultures reveals considerable variation in what children are able to do at various ages. Research has shown considerable overlap among the four stages and that development is more continuous.
Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist who wrote in the early 1900s, but whose work was not discovered by researchers in the United States until the 1960s and became more widely known in the 1980s (Crain, 2005). His sociocultural theory emphasizes the importance of culture and interaction in the development of cognitive abilities. Vygotsky differed with Piaget in that he believed that a person not only has a set of abilities, but also a set of potential abilities that can be realized if given the proper guidance from others. Vygotsky developed theories on teaching that have been adopted by educators today.
Information Processing is not the work of a single theorist, but based on the ideas and research of several cognitive scientists studying how individuals perceive, analyze, manipulate, use, and remember information. This approach assumes that humans gradually improve in their processing skills; that is, cognitive development is continuous rather than stage-like. The more complex mental skills of adults are built from the primitive abilities of children. We are born with the ability to notice stimuli, store, and retrieve information. Brain maturation enables advancements in our information processing system. At the same time, interactions with the environment also aid in our development of more effective strategies for processing information.
Urie Bronfenbrenner (1917-2005) developed the Ecological Systems Theory, which provides a framework for understanding and studying the many influences on human development (Bronfenbrenner, 1979). Bronfenbrenner recognized that human interaction is influenced by larger social forces and that an understanding of these forces is essential for understanding an individual. The individual is impacted by several systems including:
- Microsystem includes the individual’s setting and those who have direct, significant contact with the person, such as parents or siblings. The input of those is modified by the cognitive and biological state of the individual as well. These influence the person’s actions, which in turn influence systems operating on him or her.
- Mesosystem includes the larger organizational structures, such as school, the family, or religion. These institutions impact the microsystems just described. The philosophy of the school system, daily routine, assessment methods, and other characteristics can affect the child’s self-image, growth, sense of accomplishment, and schedule thereby impacting the child, physically, cognitively, and emotionally.
- Exosystem includes the larger contexts of community. A community’s values, history, and economy can impact the organizational structures it houses. Mesosystems both influence and are influenced by the exosystem.
- Macrosystem includes the cultural elements, such as global economic conditions, war, technological trends, values, philosophies, and a society’s responses to the global community.
- Chronosystem is the historical context in which these experiences occur. This relates to the different generational time periods previously discussed, such as the baby boomers and millennials.
In sum, a child’s experiences are shaped by larger forces, such as the family, schools, religion, culture, and time period. Bronfenbrenner’s model helps us understand all of the different environments that impact each one of us simultaneously. Despite its comprehensiveness, Bronfenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory is not easy to use. Taking into consideration all the different influences makes it difficult to research and determine the impact of all the different variables (Dixon, 2003). Consequently, psychologists have not fully adopted this approach, although they recognize the importance of the ecology of the individual. Figure 1.9 is a model of Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory.
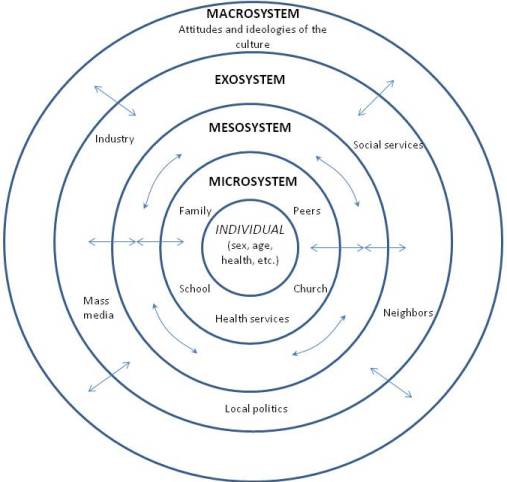
Figure 1.9. Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
Supplemental Materials
- This article discusses the importance of critical reflection on the underlying assumptions of developmental psychology as a science.
References
Baltes, P. B. (1987). Theoretical propositions of life span developmental psychology: On the dynamics between growth and decline. Developmental Psychology, 23, 611-626.
Baltes, P. B., Lindenberger, U., & Staudinger, U. M. (2006). Life span theory in developmental psychology. In W. Damon, & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology, 6th edition (pp. 569-664). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. New York: General Learning Press.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social-cognitive theory. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bandura, A, Ross, D. &. Ross S. (1963). Imitation of film-mediated aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 66, 3-11.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Crain, W. (2005). Theories of development concepts and applications (5th ed.). New Jersey: Pearson.
Crews, F. C. (1998). Unauthorized Freud: Doubters confront a legend. New York, NY: Viking Press.
Dixon, W. E. (2003). Twenty studies that revolutionized child psychology. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Erikson, E. H. (1950). Childhood and society. New York: Norton.
Guinness World Records. (2016). Oldest person (ever). Retrieved from http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/search?term=oldest+person+%28ever%29
Neugarten, B. L. (1979). Policy for the 1980s: Age or need entitlement? In J. P. Hubbard (Ed.), Aging: Agenda for the eighties, a national journal issues book (pp. 48-52). Washington, DC: Government Research Corporation.
Neugarten, D. A. (Ed.) (1996). The meanings of age. Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press.
Piaget, J. (1929). The child’s conception of the world. NY: Harcourt, Brace Jovanovich.
Smithsonian National Zoo. (2016). Retrieved from http://nationalzoo.si.edu/
Skinner, B. (1957). Verbal behavior. Acton, MA: Copley.
Skinner, B. (1968). The technology of teaching. New York, NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Skinner, B. (1972). Beyond freedom and dignity. New York, NY: Vintage Books.
Thomas, R. M. (1979). Comparing theories of child development. Santa Barbara, CA: Wadsworth.
United States Census Bureau. (2016). Poverty. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/topics/income-poverty/poverty/about/glossary.html
Vogt, W.P., & Johnson, R.B. (2016). The SAGE dictionary of statistics and methodology. Los Angeles, CA: Sage
Webb, S. J., Dawson, G., Bernier, R., & Panagiotides, H. (2006). ERP evidence of atypical face processing in young children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 884-890. doi: 10.1007/s10803-006-0126-x
Weitz, R. (2007). The sociology of health, illness, and health care: A critical approach, (4th ed.). Belmont, CA: Thomson.
OER Attribution: “Lifespan Development: A Psychological Perspective, Second Edition” by Martha Lally and Suzanne Valentine-French is licensed under a CC-BY-NC-SA-3.0
Additional written material (Meta-theories of Human Development) by Ellen Skinner, Glen Richardson, Jennifer Pitzer, and Cynthia Taylor, Portland State University is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
Media Attributions
- Private: jana-sabeth-snDUMdYF7o8-unsplash © Jana Sabeth is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Private: garrett-jackson-oOnJWBMlb5A-unsplash © Garrett Jackson is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: 6152423507_009b2626cd_o © Woody Hibbard is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Private: original © Noba Project is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- Private: Preformation is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: Sigmund_Freud,_by_Max_Halberstadt_(cropped) © Max Halberstadt is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: Erik_Erikson © Unknown is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: original © Semhur is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Private: Bronfenbrenner’s_Ecological_Theory_of_Development_(English) © Hchokr at English Wikipedia is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

